Often lesions on the skin leave scars after an invasive surgery or after a traumatic shock. Problems may occur during healing. Signs of a keloid scar are blisters and irritations. These scars need to be treated in order to be optimally healed and their appearance minimized.
What is a keloid scar?
The process of healing starts naturally when the skin is damaged. There are two distinct phenomena: regeneration of skin and consolidation of tissue.
Three distinct stages of healing exist. First, the elimination phase of both bacteria and damaged cells is taking place. The cells fill the lesion and start providing collagen and blood vessels to progressively replenish the skin.
Keloid is a benign skin condition. Sometimes the skin does not recover normally during the repair of a lesion. Fibrous blisters develop, causing a significant accumulation on the scar, depending on the patient's complexion, a red or dark brown skin growth.
Keloids can often be irritating or itchy even though they're harmless and not infectious. In particular, we are talking about keloid scars as they last more than 18 months and exceed the initial scar surface.
What causes a keloid scar?
Keloids occur primarily on skin lesions: post-surgery scars, cuts, acne scars, bites, or piercings.
When anomalies occur during the healing process keloids appear. Excessive fibrous tissue is formed by skin cells. The quantity of collagen in the skin increases the height and thickness of the scar and is becoming rough and fibrous.
This phenomenon affects teens and pregnant women in particular. In people from 20 to 30 years of age, there are a large number of keloids. The skin tones of Asians, mixed races and blacks are more vulnerable to this abnormality. In Caucasian people, this overhealing is less common.
Treatment of keloid scars
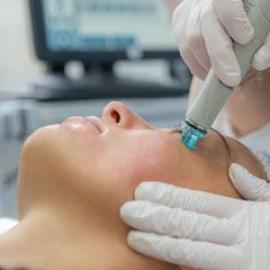
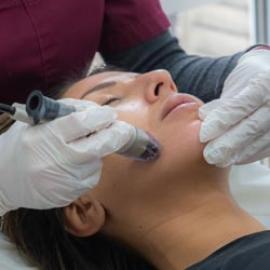
In aesthetic medicine, there are treatments that decrease or remove keloids on any scars that do not naturally fade away.
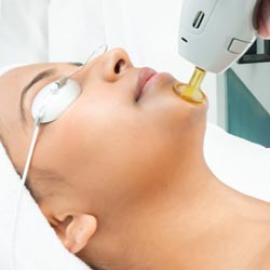
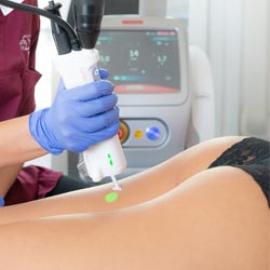
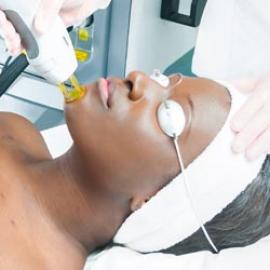
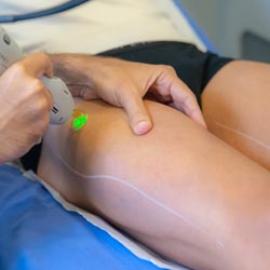
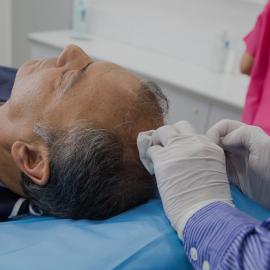
Lasers are the most effective method of extracting keloids. It operates on the principle that a pulsed light beam is projected onto the scar. A non invasive procedure, which uses dermabrasion to destroy excess tissue, is a CO2 laser, or Erbium laser. The laser transforms energy and eliminates the keloid as it comes into contact with the skin. Depending on the size of the keloid, several sessions may be required.
The Plexr® plasma energy also results in excellent results for small keloids.