In our modern culture, sweating is not an acceptable esthetic or hygienic norm, yet perspiration is a natural phenomenon. Excessive sweating, however, is rather socially limiting and can become a source of insecurity, which is why cosmetic medicine provides certain treatments.
Excessive sweating: definition
It is difficult to clearly describe the difference between normal levels of sweating and excessive sweating.
Sweating is part of the body's normal function. The sweat glands produce a clear, aqueous liquid that controls the body's temperature and, in particular, cools it down to a temperature of 37°C. There is perspiration in the armpits and the scalp and the back.
Sweating is caused by a number of factors: sport or physical activity, ambient heat or stress.
Hyperhidrosis or excessive sweating means that too much sweat is generated. Any sweating that goes beyond what is necessary or is uncontrollable and inconvenient is called 'excessive.' Hyperhidrosis affects every area that sweat, particularly the hands and feet.
Excessive sweating: the causes
Hyperhidrosis causes are attributed to overactive sweat glands. The hypothalamus, the nucleus of our brain, sends all the stimuli required for sweating. As the temperature of the body increases, the hypothalamus activates the sweat glands in the dermis, causing the arteries to dilate and to create sweat on the surface of the skin.
In cases of excessive sweating, the sweat glands are no longer controlled and generate excess watery liquid after physical exercise, intense heat or severe stress.
This physiological abnormality does not pose a health danger, but may be a major source of hang-ups.
Excessive sweating: treatment
You need to see a specialist in order to treat excessive sweating.
Firstly, it is possible to resolve hyperhidrosis with treatments you apply locally. These products are antiperspirants containing aluminum chloride. They are applied primarily to the armpits as a deoderant, which ensures that aluminum chloride is accumulated on the sweat ducts and limits the flow of sweat to the surface of the skin.
It is also possible to cure excessive sweating by using electrodes. Lontophoresis seeks to reduce perspiration, especially on the hands and feet, by immersing them in water tanks where low electrical current is diffused.
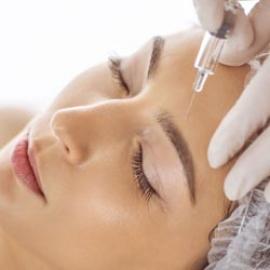
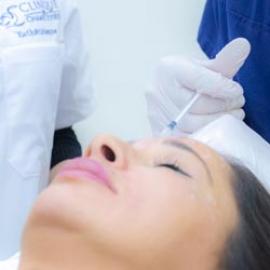
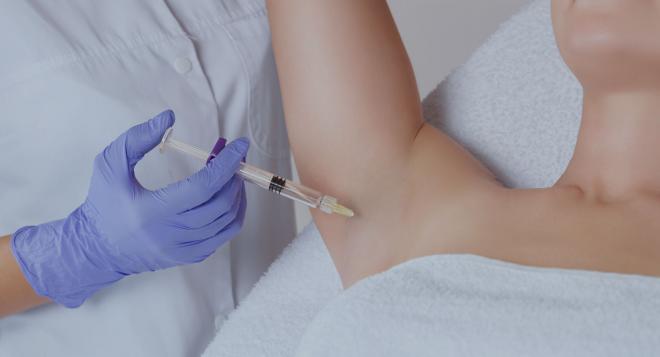
Other possible treatments include botulinum toxin (Botox) injections in the armpits, face, hands or feet to reduce the amount of sweat produced. Botulinum toxin inhibits activation of the sweat glands. This procedure is used in severe cases of hyperhidrosis.
Finally, it is possible to cure excessive sweating with surgery. This includes separating the sympathetic glands by means of an endoscope to split the nerve ends that supply the sweat glands. The glands then produce less sweat since they obtain less input. In the most serious cases, part of the sweat gland can be removed.